Choosing the right downlight feels complicated. You worry that picking the wrong one will waste energy and money. The real secret to efficiency isn’t just about the wattage you see.
The most energy-efficient downlight is not just the one with the lowest wattage. It’s the one with the highest optical efficiency, meaning its beam angle perfectly matches the task. This ensures every bit of light is used effectively, instead of being wasted on walls or ceilings.

Everyone looks at the watts on the box. It seems simple. Lower watts mean lower bills. But that’s only half the story. I’ve seen clients spend a fortune on "efficient" lights that still waste a huge amount of energy. The real magic happens when you look at where the light actually goes. Let’s dive deeper into what truly makes a downlight efficient and how you can make the best choice for your project.
Will I notice a difference between LED and OLED?
You’re looking at lighting options and see LED and OLED. You wonder if the choice really matters. Picking the wrong one can change the entire feel and cost of a project.
Yes, you will absolutely notice a difference. LEDs are tiny, powerful point sources of light, perfect for focused beams like in downlights. OLEDs are thin, flat panels that produce a soft, diffuse glow, ideal for gentle, area lighting. They serve very different purposes.
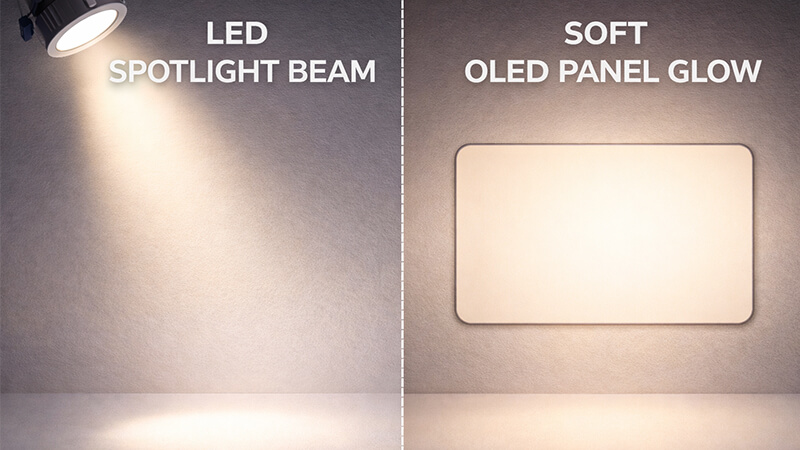
When I first started in this industry, the technology was changing fast. Now, the difference between LED and OLED is a great example of how specific lighting can be. Think of an LED like a laser pointer. It’s intense and focused. This is why nearly all downlights, spotlights, and task lights use LEDs. We need that power to direct light exactly where it’s needed, like onto a kitchen counter or a piece of art. The ability to control the beam with lenses and reflectors is what makes LEDs so versatile and efficient for these jobs.
OLEDs are the opposite. Imagine a glowing sheet of paper. The light is soft, even, and doesn’t create harsh shadows. It’s beautiful for creating ambient light or for unique, high-end fixtures where you want the light source itself to be a design element. However, they are not as bright or efficient as LEDs, and they are much more expensive. For the specific job of a downlight, LED is the clear winner in every category.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Feature |
LED (Light Emitting Diode) |
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) |
| Light Type |
Point Source (Intense, focused) |
Area Source (Soft, diffuse) |
| Best Use |
Downlights, spotlights, task lighting |
Ambient lighting, decorative fixtures |
| Efficiency |
Very high (lumens per watt) |
Moderate |
| Cost |
Low to moderate |
Very high |
| Lifespan |
Very long |
Moderate to long |
For a purchasing manager like Shaz, the choice is clear for 99% of projects. When you need effective, efficient, and affordable downlights, LED is the only practical technology.
Which lights are most energy-efficient?
The market is full of lights claiming to be "green" and "efficient." It’s confusing to know which claims are real. Making the wrong choice means you are not getting the savings you expect.
LEDs are, by a large margin, the most energy-efficient lights widely available today. They use up to 90% less energy than old incandescent bulbs and last over 25 times longer. They are the clear winner for saving electricity and reducing maintenance costs.

I remember when my clients first started asking about LEDs. They were expensive back then. The initial cost was a barrier. But I showed them the long-term math. I worked with a project manager who was retrofitting a large office building. They were using hundreds of 50-watt halogen downlights. The lights were hot, burned out all the time, and the electricity bills were huge. We replaced every single one with a 7-watt LED downlight that produced the same amount of light.
The result was immediate. Their monthly electricity bill for lighting dropped by over 80%. But the savings didn’t stop there. Their maintenance team, which used to spend hours each week on ladders changing bulbs, could now focus on other tasks. We calculated that over five years, the project would save them hundreds of thousands of dollars, not just in energy but in labor and replacement bulbs. That’s the power of switching to LED. They are simply in a different league compared to older technologies.
Let’s look at the numbers for a standard light bulb equivalent:
| Light Type |
Energy Usage (Watts) |
Average Lifespan (Hours) |
Key Feature |
| Incandescent |
60W |
1,000 |
Cheap to buy, very inefficient |
| Halogen |
43W |
2,500 |
Slightly better than incandescent |
| CFL |
13W |
10,000 |
Efficient, but contains mercury |
| LED |
7W-9W |
25,000 – 50,000 |
Most efficient, longest lasting |
While LED is the most efficient technology, my main point stands. The most efficient solution is using the right LED for the job. In that office building, we didn’t just install one type of LED. We used downlights with a narrow 24° beam over desks and wider 60° beam lights in the hallways. We made sure the efficient light was also used effectively.
What wastes the most electricity in a house?
You get your power bill and it’s higher than you want. You are sure something is wasting electricity. But you can’t figure out what the biggest problems are in your home.
Heating and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are the biggest energy users in most homes, often accounting for nearly half of your bill. Water heaters are usually second. Inefficient lighting, especially old bulbs, is also a significant and easily fixable source of waste.
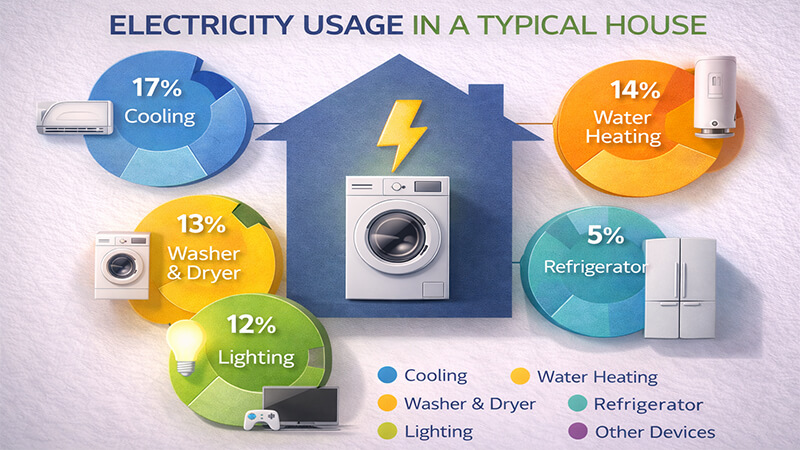
We all think about turning off the lights to save energy. And we should. But it helps to know where the big wins are. Your home’s HVAC system works hard to keep you comfortable, and that takes a massive amount of power. The same goes for heating water. These two things are almost always the top energy consumers. After that, you have your large appliances like refrigerators, clothes dryers, and ovens.
So where does lighting fit in? It typically accounts for about 5-10% of a home’s total electricity use. That might not sound like much compared to your air conditioner, but it’s what I call "low-hanging fruit." Upgrading your lighting is one of the fastest, easiest, and most affordable ways to start saving money immediately. You can’t easily replace your entire HVAC system, but you can change a light bulb in a few minutes.
I did this in my own home. I went through and replaced every old bulb with an LED. The savings on my bill were noticeable right away. But I took it a step further. In my kitchen, I used downlights with a tight beam angle directly over the counters where I chop vegetables. This meant I didn’t need as many lights to see clearly. In my living room, I used wider beam angles for soft, general light. This concept is called "light layering," and it is the key to both beautiful and efficient design. By putting the right amount of light exactly where it is needed, I waste nothing. That’s true efficiency.
Is anything 100% energy efficient?
We always search for the perfect product. We want something that wastes nothing. It’s frustrating when you learn that even the best technology has its limits. The truth is a bit more complicated.
No, according to the laws of physics, nothing can be 100% energy efficient. During any energy conversion, some energy is always lost to another form, most commonly as heat. Even the best LEDs lose more than half their energy as heat, not light.

This is a fundamental concept that’s really important in my line of work. When you power a light bulb, you are converting electrical energy into light energy (lumens). But the process is never perfect. A lot of that electrical energy gets converted into heat instead.
An old incandescent bulb is a perfect example of bad efficiency. It’s really just a heater that happens to produce a little bit of light as a side effect. About 90% of the electricity it uses is wasted as heat. You can feel this if you ever try to touch one that’s been on for a while.
LEDs are champions of efficiency in comparison, but they still aren’t perfect. A typical high-quality LED might convert 40% to 50% of its electrical energy into light. The other 50% to 60% is lost as heat. This is why good LED downlights have big metal heat sinks on the back. That metal is there to pull the waste heat away from the delicate LED chip. If that heat isn’t managed properly, the chip will overheat and its lifespan will be drastically shortened. This is why cheap, poorly designed LEDs fail so quickly.
Since we can never get to 100% conversion efficiency, we have to focus on what I call "application efficiency." My core insight is this: if we can’t stop the light from wasting energy as heat, we must at least make sure that every single lumen it produces is used perfectly. This means not wasting light by spilling it onto a wall or ceiling where it isn’t needed. A downlight that uses a 24° beam to perfectly light a dining table is infinitely more efficient than a 60° beam light that lights the table and half the floor around it. This focus on optical precision is how we achieve true, practical efficiency.
Conclusion
True downlight efficiency isn’t just about low watts. It’s about combining efficient LED technology with smart optical design, ensuring the right light goes exactly where you need it.